A dead tooth not only can cause pain locally and in surrounding gums but may also change in color — degrading the quality of your smile. Left untreated, a dead tooth can spread bacteria to nearby teeth and gums, increasing the risk of infection and tooth loss. If you experience one or more symptoms of a dead tooth, visit your dentist right away so you can potentially save the tooth, resolve related pain and discomfort, and prevent the tooth from causing additional oral health problems.
What constitutes a dead tooth? What does a dead tooth look like? How can you identify the symptoms of a dead tooth, and what should you do if you find these symptoms?
Table of Contents
Dead Tooth Symptoms
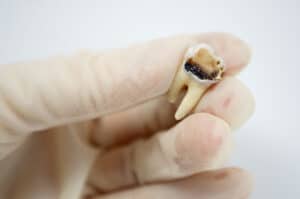
Other symptoms of a dead tooth may include:
- Bad breath
- Bad smell coming from the tooth
- Unpleasant taste in the mouth
- Swelling around the gum line near the affected tooth
- Inflamed sore on the gums
- Pimple on the gum line
If experience one or more of these symptoms of a dead tooth, make an appointment with your dentist as soon as possible.
Dead Tooth Causes
Tooth decay, trauma, and injury represent the main causes of a dead tooth.
Tooth decay can be caused by factors including poor oral hygiene (not brushing and flossing regularly), a diet high in sugary foods and junk foods, and the use of certain medications. Cavities will gradually eat away at tooth enamel and eventually reach the pulp — where the restricted blood supply to the tooth results in a dead tooth.
Trauma and injury to a tooth — such as that caused by contact sports or a blow to the face — can rupture blood vessels that control blood flow to the tooth. This can prevent tooth nerves from receiving the oxygen and nutrition they need, causing the tooth to die.
Dead Tooth Treatments
Getting a treatment can prevent bacteria from spreading from the dead tooth to nearby teeth, gums, and the jawbone — causing additional decay, infection, and tooth loss. A root canal or tooth extraction can often effectively treat a dead tooth.
During a root canal, your dentist performs a deep cleaning of the inside of the affected tooth to remove its pulp and infected tissue. Though your tooth may be dead, it can still be useful as long as it is not chipped or broken, reports MedlinePlus. In some cases, a dental crown may be implanted to support and strengthen a dead tooth.
If extremely brittle, broken, or severely damaged, tooth extraction may be performed. If the dead tooth must be completely extracted, your dentist may recommend replacing the tooth with a denture, implant, or bridge that can help you maintain oral functionality.
Dead Tooth FAQs
What is a dead tooth?
A dead tooth has stopped receiving fresh blood supply. Lack of blood flow to a tooth can cause it to die and become discolored, infected, chipped, and/or broken. People with a dead tooth may experience pain and discomfort in and around the tooth and display yellow, gray, or black discoloration of the tooth.
What causes a dead tooth?
The most common causes of a dead tooth include tooth decay, trauma, and injury. Poor oral hygiene can cause tooth decay; traumatic injury leading to a dead tooth may stem from receiving a blow to the face, tripping and falling, and participating in contact sports.
How can I tell if a tooth is dead?
A dead tooth may cause mild to severe pain in and around the affected tooth and gum line. Other signs and symptoms of a dead tooth include tooth discoloration, bad breath, a bad taste in the mouth, swelling around the tooth, and a pimple or abscess on the gum line near the tooth.
What does a dead tooth look like?
A dead tooth will often gradually become discolored as a result of stopped blood flow to the tooth. A dead tooth may appear yellow, gray, or black, and may also become brittle, chipped, and/or broken.
Can you save a dying tooth?
A root canal may salvage a dead or dying tooth. A root canal gives your dentist the opportunity to clean the inside of the affected tooth and remove pulp and infected tissues contributing to pain, discomfort, and other related symptoms. If a dying tooth cannot be completely saved, your dentist may perform extraction or recommend a dental implant to support the structure and functionality of the tooth.
Sarasota Dentistry offers root canal and tooth extraction treatments. If you have a dead tooth or exhibit symptoms, contact our office today at 941-929-7645 to schedule an appointment and to learn more about your available treatment options.
- Dental Implant Pros and Cons - August 26, 2023
- Receding Gums Stages - August 12, 2023
- When Is It Too Late for Gum Grafting? - July 8, 2023


